Electronic Kits & Parts
Ordering & shipping charges

|
Electronic Kits & Parts |
|
Ordering & shipping charges |
 |
Calculation of LED current limiting resistors (#80228)
When connecting LED to higher DC voltage, it is necessary to add a series resistor in order to limit the LED current to a safe level. This is to avoid damaging the LED due to excessive current. In the following short discussion, we shall demonstrate by way of examples how the value of the resistor can be calculated (in different situations) using simple math & Ohm's Law.
Example (1) : Connecting a common red LED of to DC 6V
| Red
LED of normal brightness typically has forward voltage of around 1.5V. In this example,
we set current to 10 mA. The voltage (VR) across the resistor R is : VR = Vs - VLED = 6V - 1.5V = 4.5V By Ohm's Law the resistor value R = VR / I = 4.5V / 0.01A = 450 Ω For convenience we will select a 470 Ω standard resistor which is easier to get the the market. With this resistor the actual current would be I = VR / R = 4.5V / 470 Ω = 0.0096A (or 9.6mA) What size of resistor to use ? The wattage of resistor can be calculated using the equation P = V2 / R Here we have P = VR2 / 470 Ω = (6 - 1.5)2 / 470 = 0.043W. So, both 1/4W & 1/6W resistors can be used ( 1/4W=0.25W & 1/6W=0.167W. Both are larger than 0.043W) |
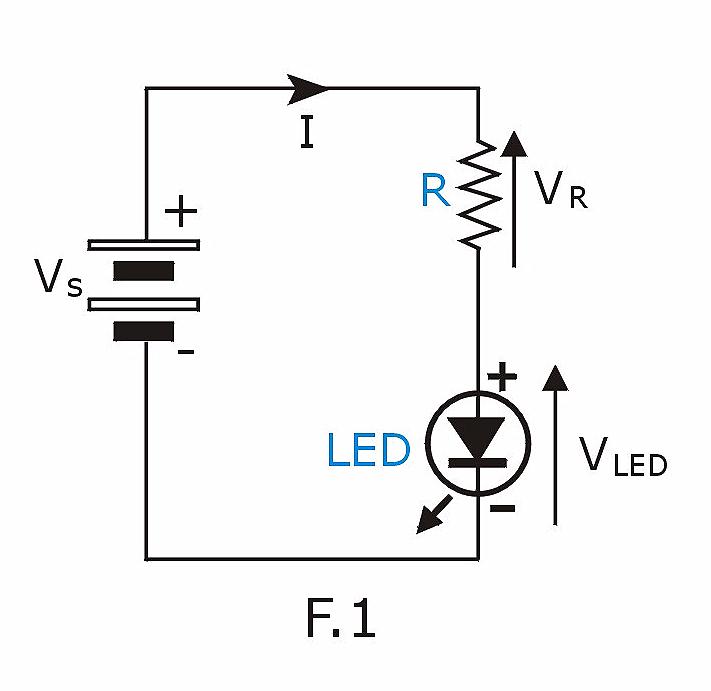 |
Example (2) : Connecting 3 super bright white LED to DC 12V
| The
voltage of white super bright LED is around 3V. Let us set the
LED current to 30 mA which is quite standard for super bright LED The voltage across the
resistor R is : VR = Vs - (3 x VLED
) = 12V - (3 x 3V) = 3V |
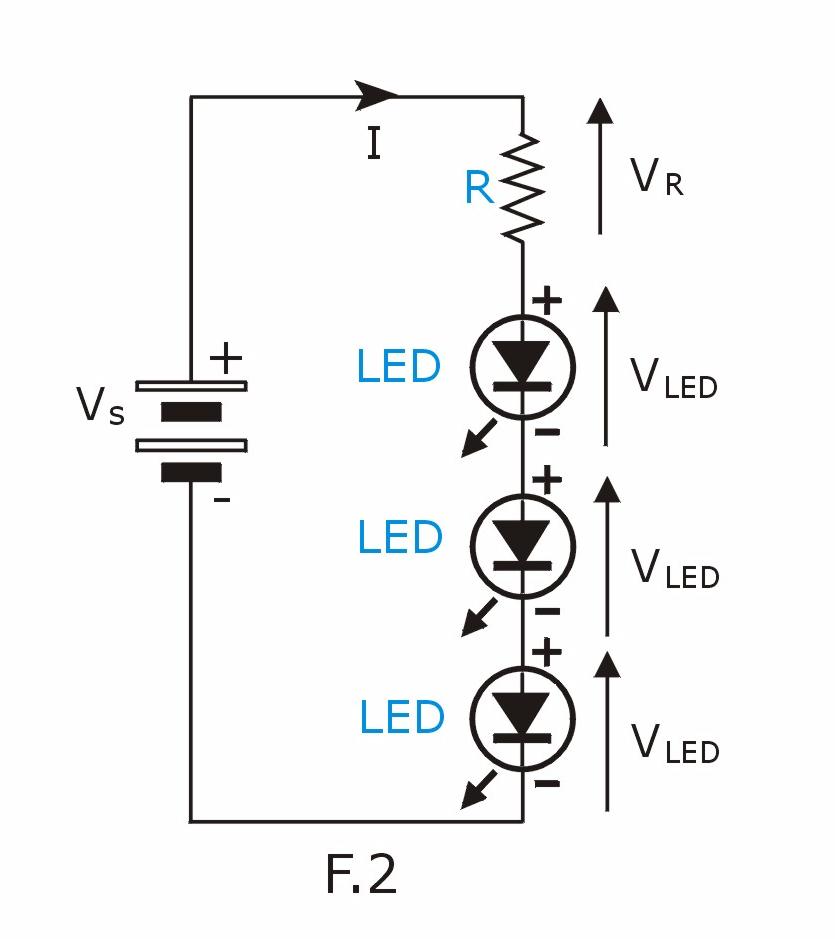 |
Example (3) : Connecting 9 super bright blue LED to DC 12V
|
Blue & white super bright LED has the same forward voltage
which is around 3V, so we will be using the same resistor (100
Ω) from example(2)
Here we
connect 3 strings of LED in parallel each
consists of 3 LED and a resistor. You can have more LED by adding additional strings of LED but you have to make sure that the DC supply (or battery) is able to provide the increased current
NOTE : The brightness of the LED is proportional to the current that flows thru it. That is, the higher the current, the brighter the LED but it should be limited within a safe level to avoid damaging or shortening the life of the LED. |
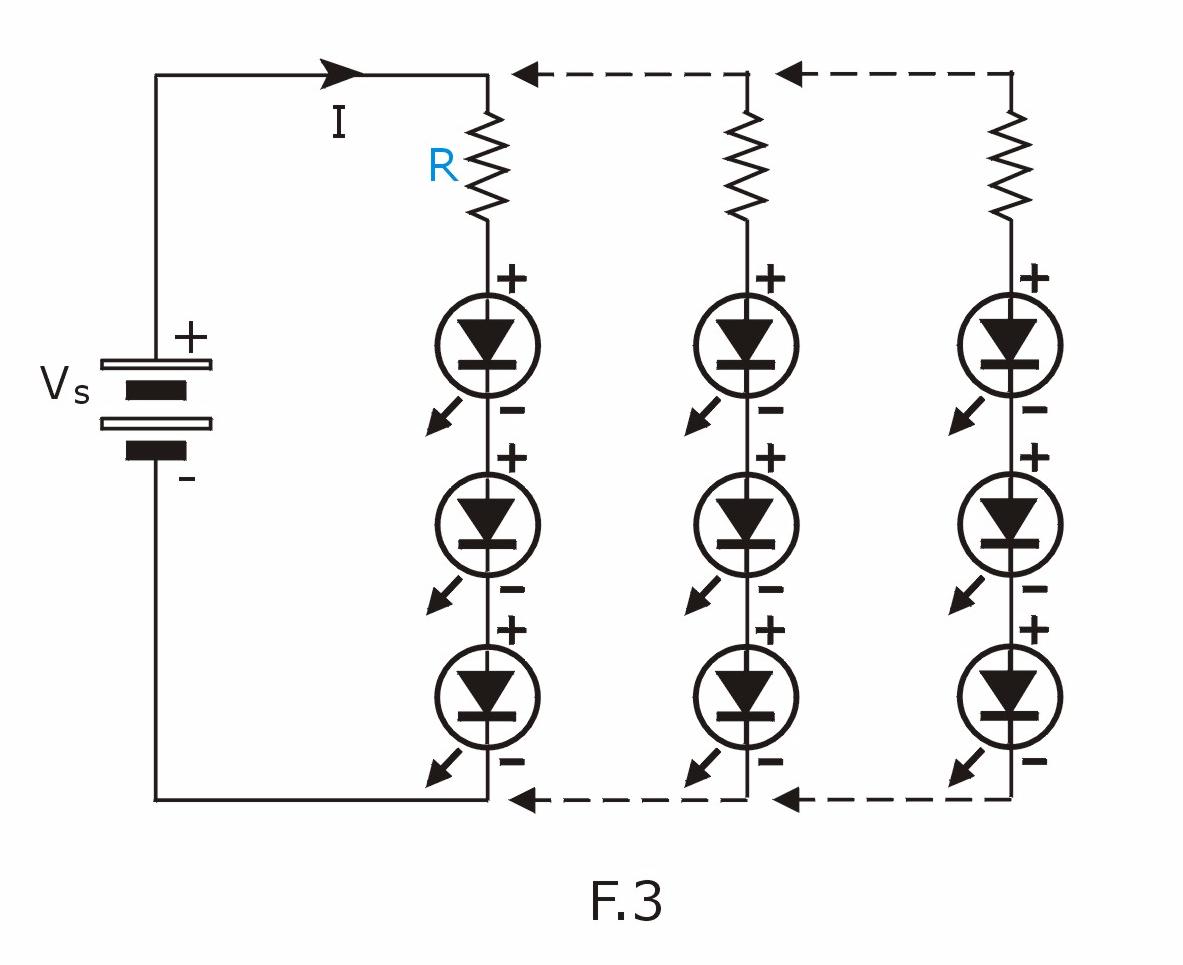 |